|
I'm a fourth year CS PhD student in Berkeley EECS advised by Dan Klein. Previously, I was a UC Berkeley undergrad, where I had the great opportunity to work with and learn from a number of fantastic AI researchers, such as Sergey Levine, Ruiqi Zhong, Dan Klein, Jacob Steinhardt, and Jason Eisner. I was also previously a Student Researcher at Google DeepMind. I am now working at Cursor on training frontier coding agents. Email / Google Scholar / Twitter / Github |

|
|
See Google Scholar for more. |
|
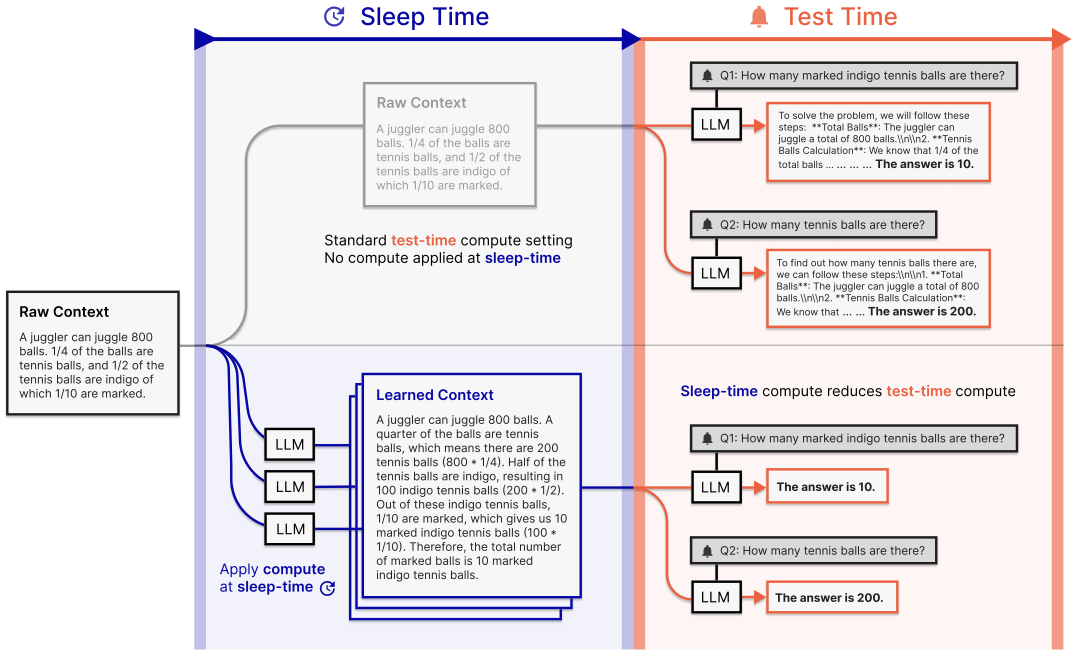
Kevin Lin*, Charlie Snell*, Yu Wang, Charles Packer, Sarah Wooders, Ion Stoica, Joseph E. Gonzalez ArXiv 2025 [paper] We introduce sleep-time compute, which allows models to “think” offline about contexts before queries are presented: by anticipating what queries users might ask and pre-computing useful quantities, we can significantly reduce the compute requirements at test-time. |
|
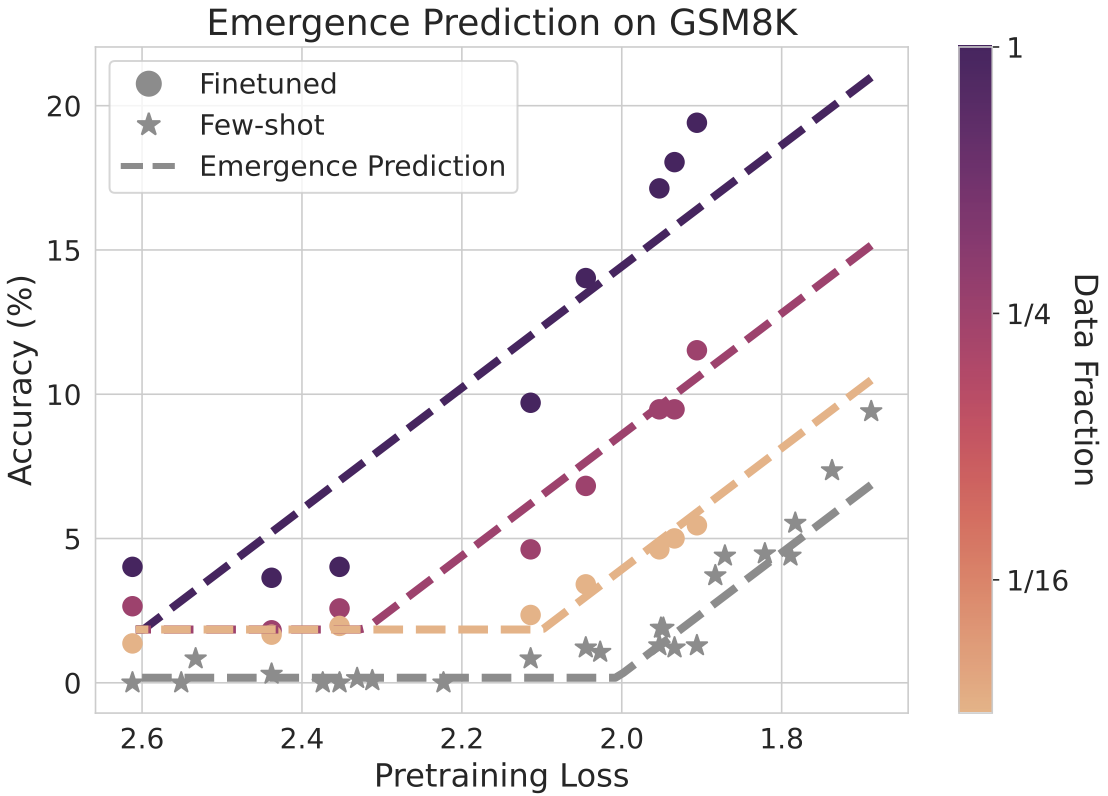
Charlie Snell, Eric Wallace, Dan Klein, Sergey Levine COLM 2024 [paper] Can we predict emergent capabilities in GPT-N+1 🌌 using GPT-N, which has random performance on the task? To do this, we use information about how pre-emergence model checkpoints behave under the influence of task-specific finetuning to obtain predictive power about the point of emergence in the few-shot setting. |
|
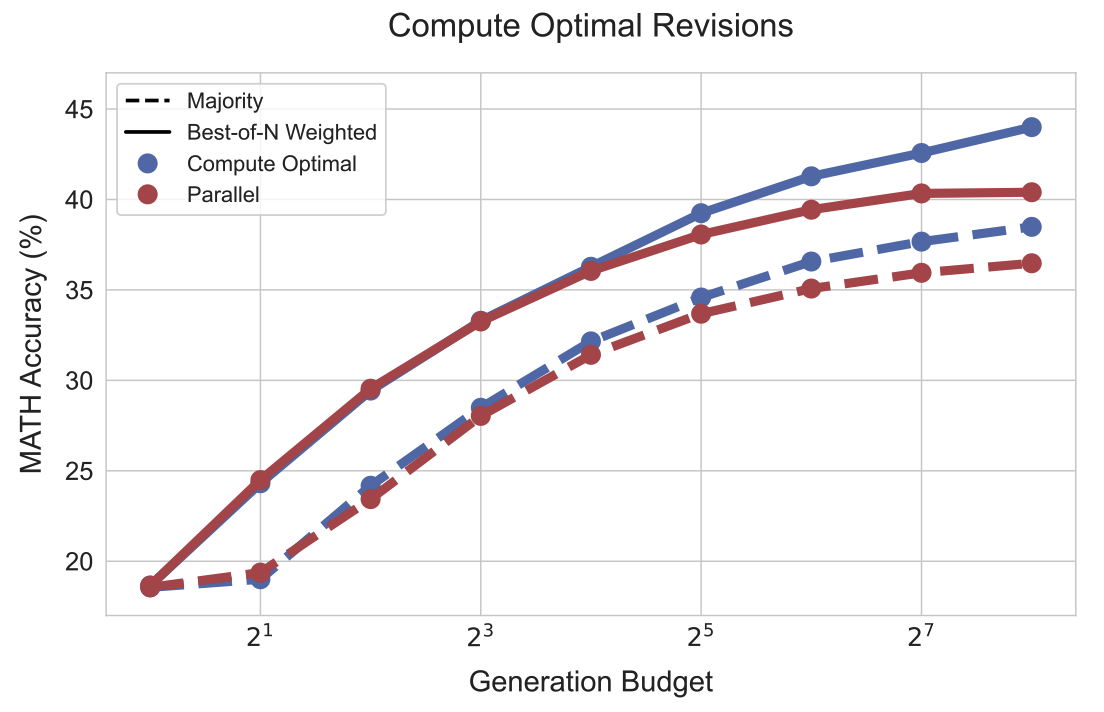
Charlie Snell, Jaehoon Lee, Kelvin Xu, Aviral Kumar arXiv 2024 [paper] On difficult problems, humans tend to think longer to improve their decisions. Can we instill a similar capability into LLMs? And how well can it perform? We find that by optimally scaling test-time compute we can outperform much larger models in a FLOPs matched evaluation. |
|
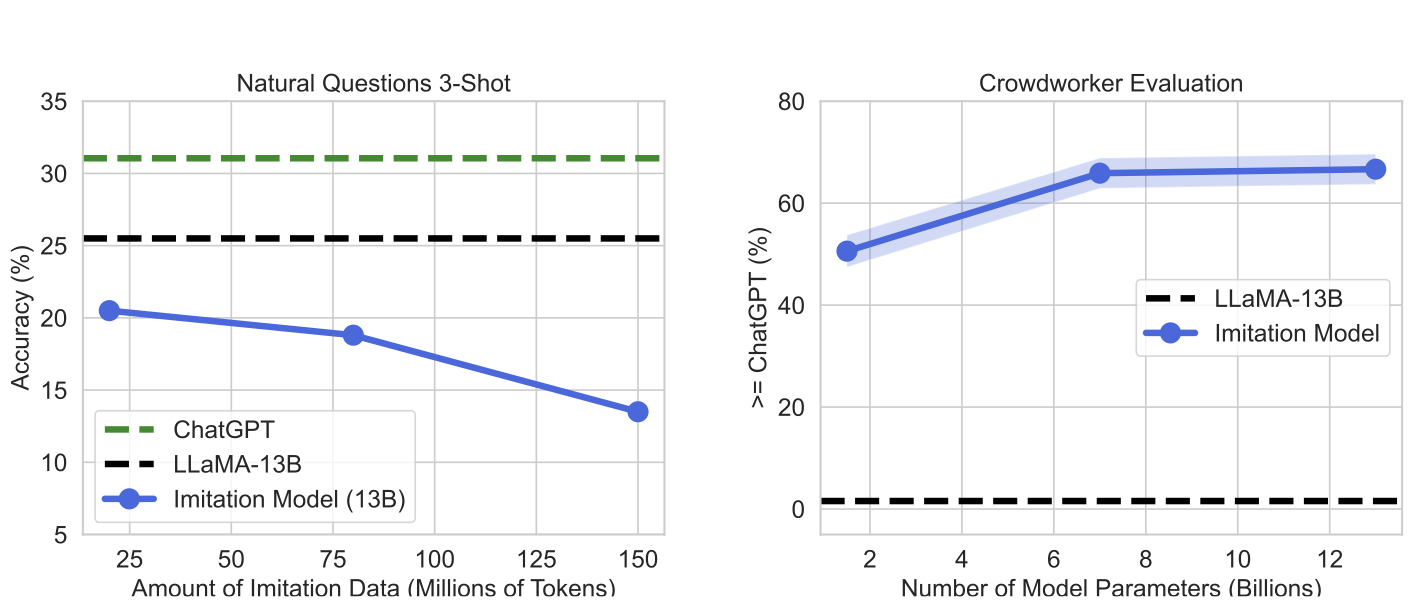
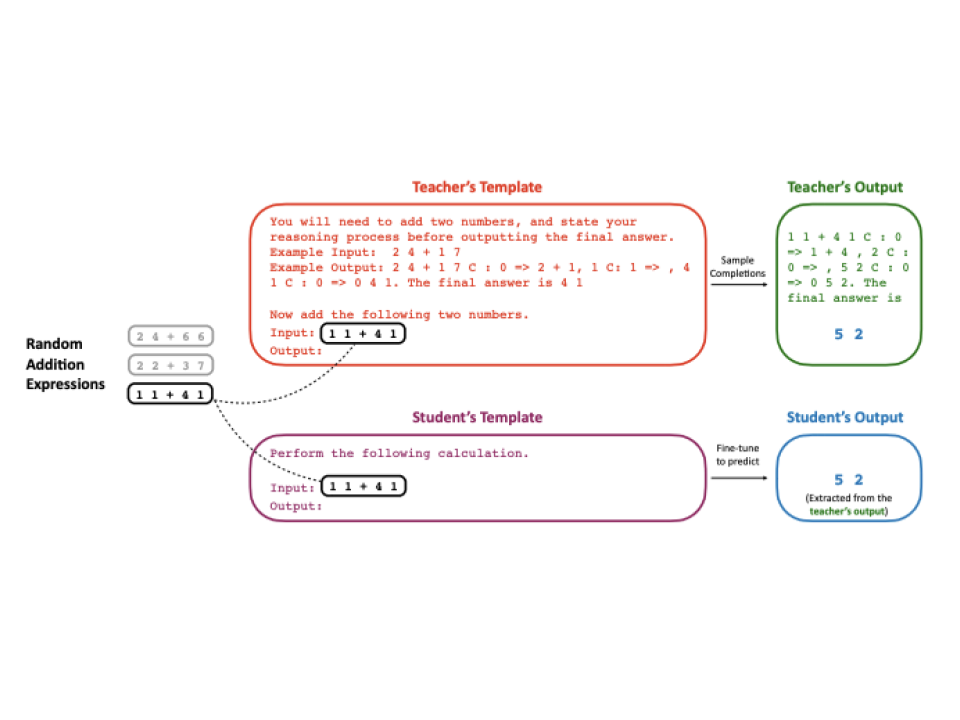
Arnav Gudibande*, Eric Wallace*, Charlie Snell*, Xinyang Geng, Hao Liu, Pieter Abbeel, Sergey Levine, Dawn Song ICLR 2024 [paper] Recent systems – like Koala, Vicuna, and Alpaca – finetune a weaker language model to imitate the outputs of a stronger model, like ChatGPT or GPT-4. In this work, we critically analyze the shortcomings of this approach. |
|
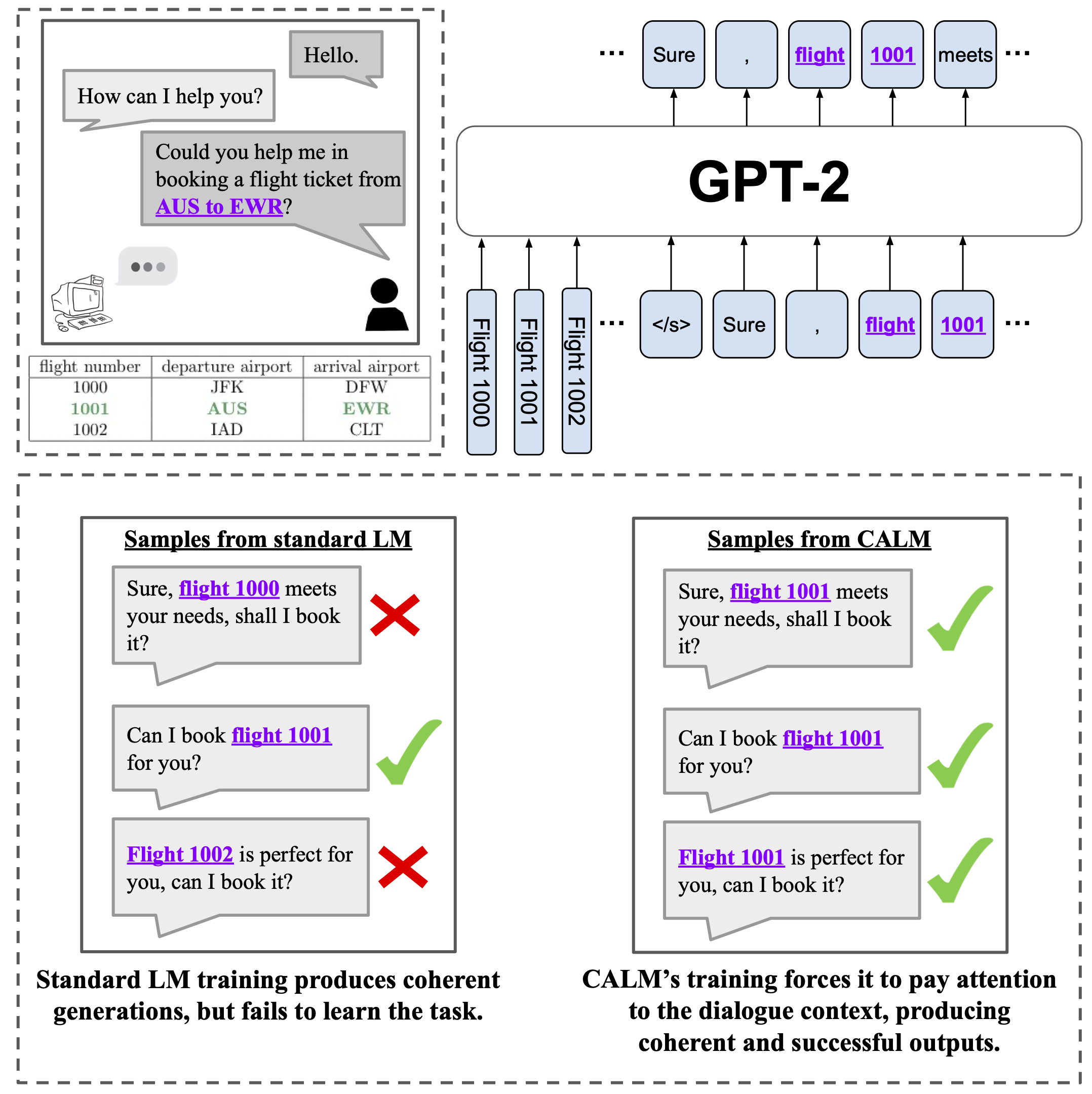
Charlie Snell, Dan Klein, Ruiqi Zhong arXiv 2022 [paper] [talk] Language models significantly benefit from context tokens, such as prompts or scratchpads. We propose to apply context distillation so that a language model can improve itself by internalizing these gains. |
|
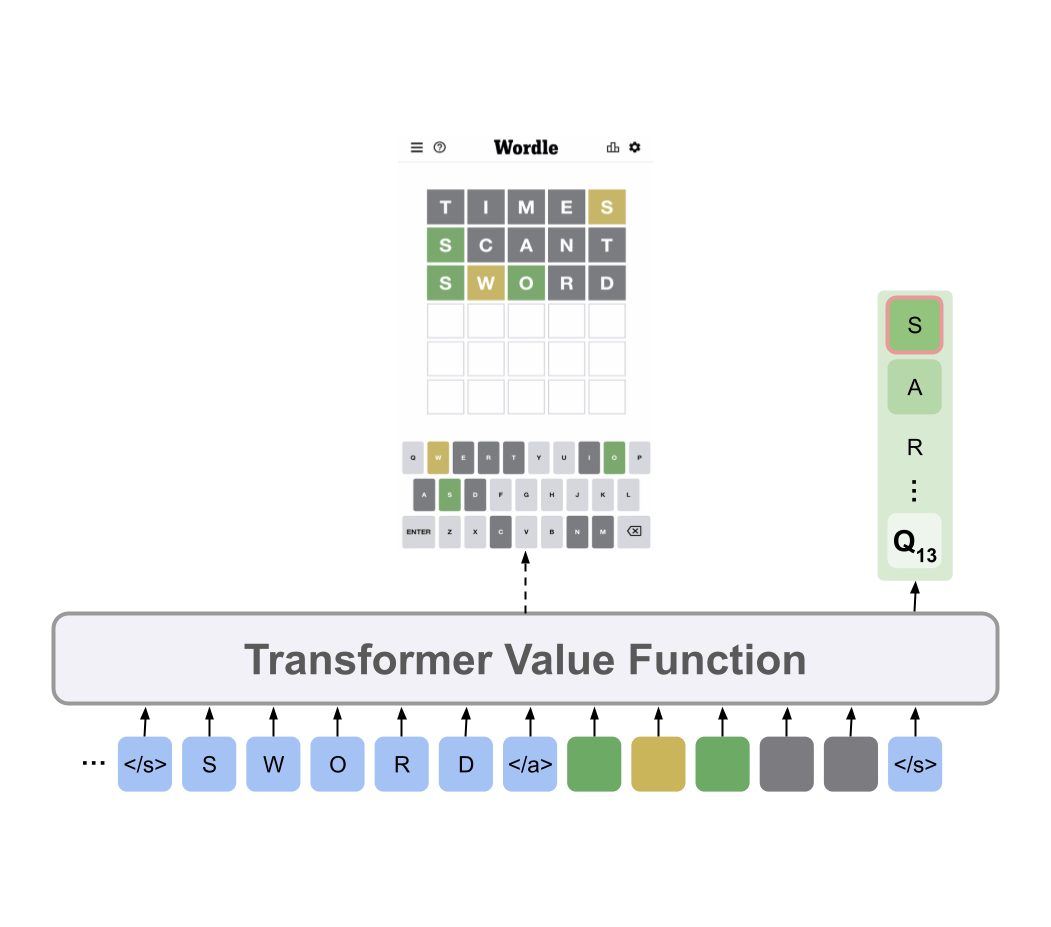
Charlie Snell, Ilya Kostrikov, Yi Su, Mengjiao Yang, Sergey Levine ICLR 2023 [paper] [project page] [code] [talk] We propose an effective and easy-to-use offline RL motivated method for steering language models towards successfully completing language tasks, such as goal directed dialogue, controled generation, and word games. |
|
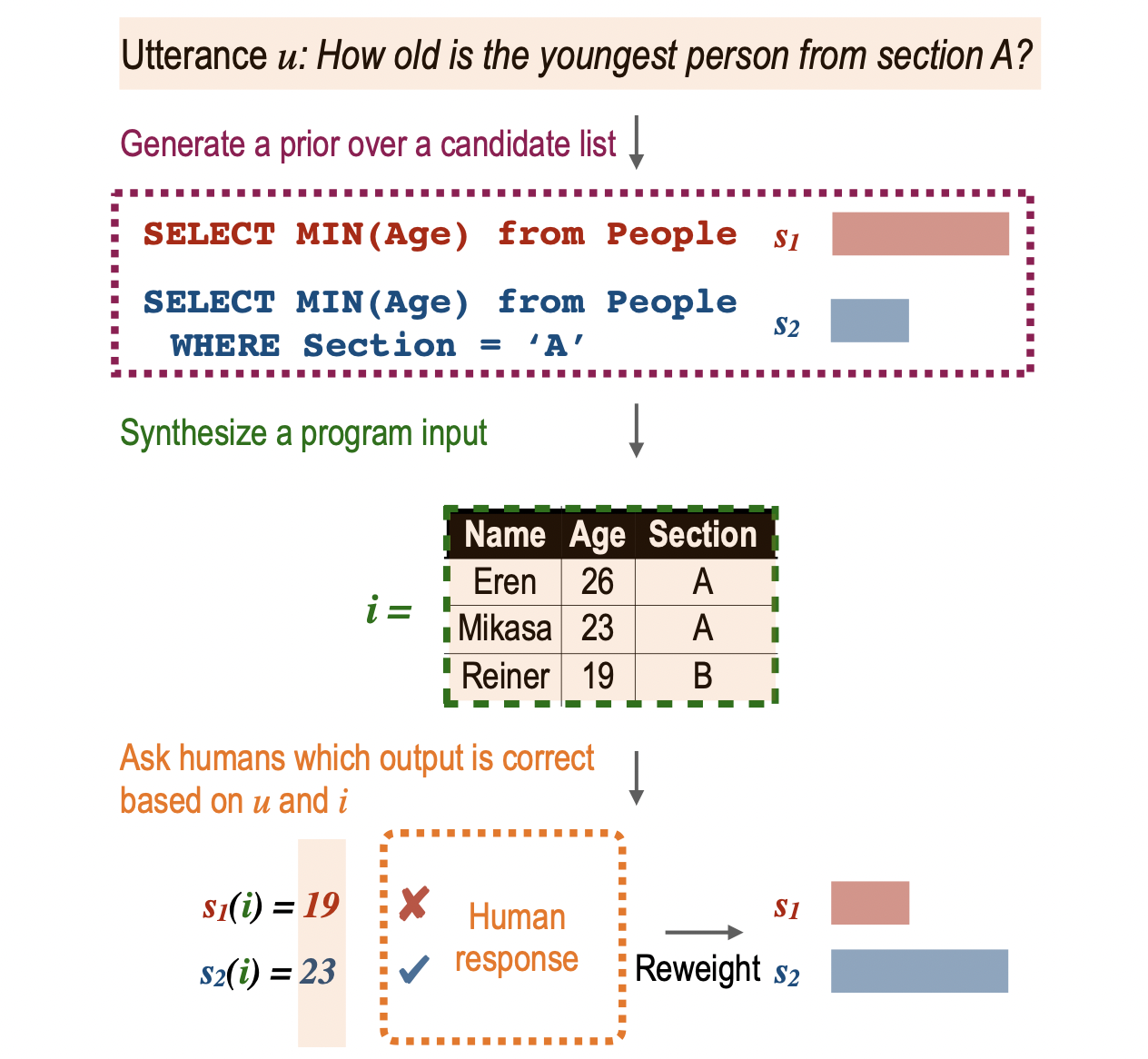
Ruiqi Zhong*, Charlie Snell*, Dan Klein, Jason Eisner EMNLP 2023 [paper] We introduce APEL, a new framework that enables non-programmers to indirectly annotate natural language utterances with executable meaning representations, such as SQL programs. |
|
Charlie Snell, Mengjiao Yang, Justin Fu, Yi Su, Sergey Levine NAACL 2022, Findings [paper] [project page] [code] We extend techniques from learning-based control, such as task relabeling, to derive a simple and effective method to finetune language models in a goal-aware way. |
|
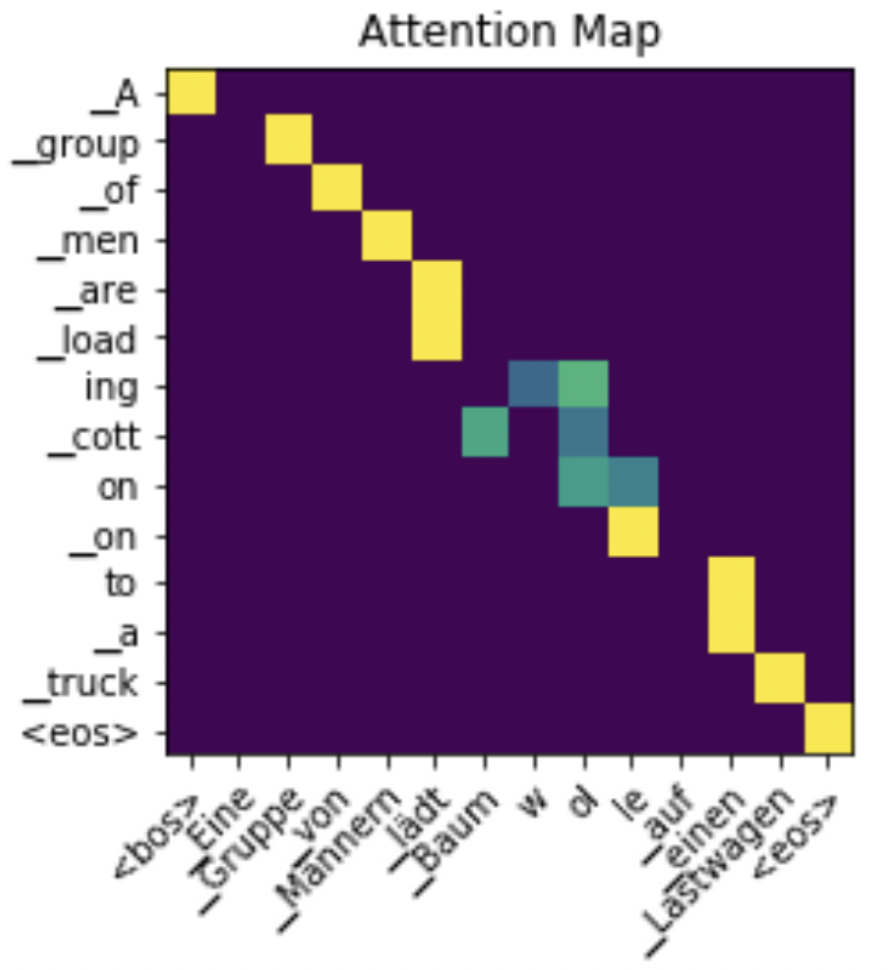
Charlie Snell*, Ruiqi Zhong*, Dan Klein, Jacob Steinhardt arXiv 2021 [paper] [slides] [code] [blog] Why do models often attend to salient words, and how does this evolve throughout training? |

|
Eliza Kosoy, Masha Belyi, Charlie Snell, Josh Tenenbaum, Brenden Lake, Alison Gopnik NeurIPS Workshop on BabyMind 2020 [paper] We augment the original Omniglot dataset with a new dataset of children's handwritten characters. We then study the properties of a Bayesian Program Learning model trained on this new data. |
|
I've had the pleasure of getting to write several articles for Machine Learning at Berkeley's technical blog. |

|
June 2021 [blog] [coverage] [discussion] A tour through the wonderful AI art scene that emerged when CLIP was released in January 2021. |

|
April 2021 [blog] A technical and philosophical discussion of how DALL-E works, why it is so effective at generating images from a text prompt, and its theoretical limitations. |
|
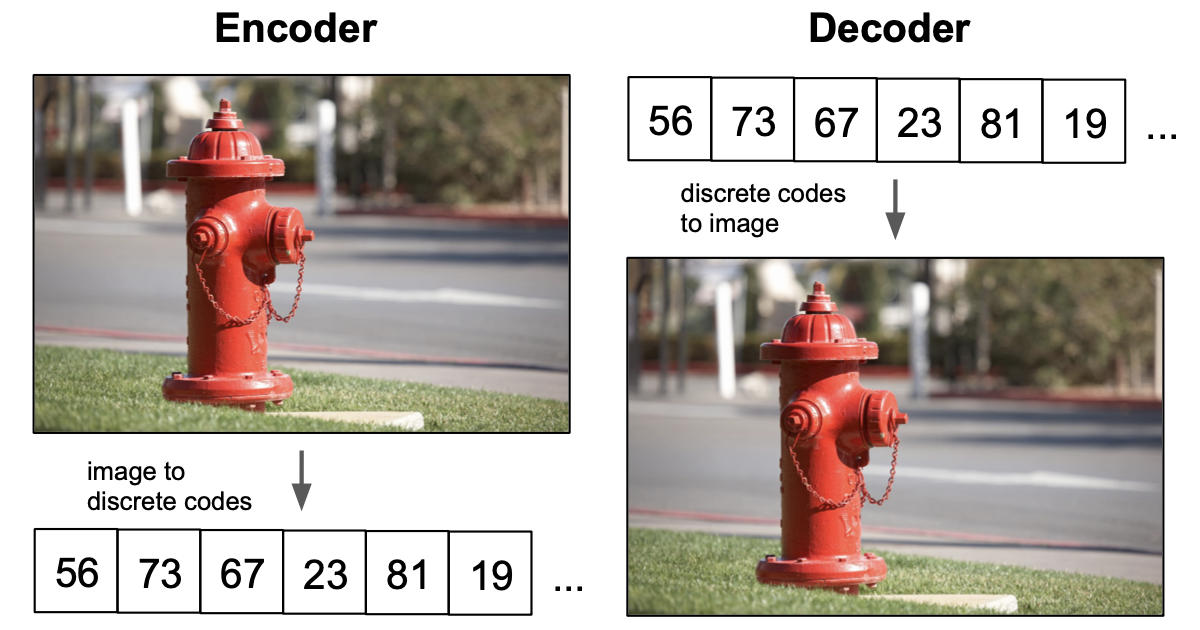
February 2021 [blog] How do vector quantized variational autoencoders (VQ-VAEs) work? And what role do they play in modern generative models, such as DALL-E and Jukebox? |
|
Selected projects. See my github for much more. (Press "y" to add a random circle, "n" to remove one, and "wasd" to pan.) |
|
October 2022 [code] Built on top of HuggingFace's Transformers library, JaxSeq enables training very large language models in Jax with model and data parallelism across both multi-device and multi-node clusters. |
|
|
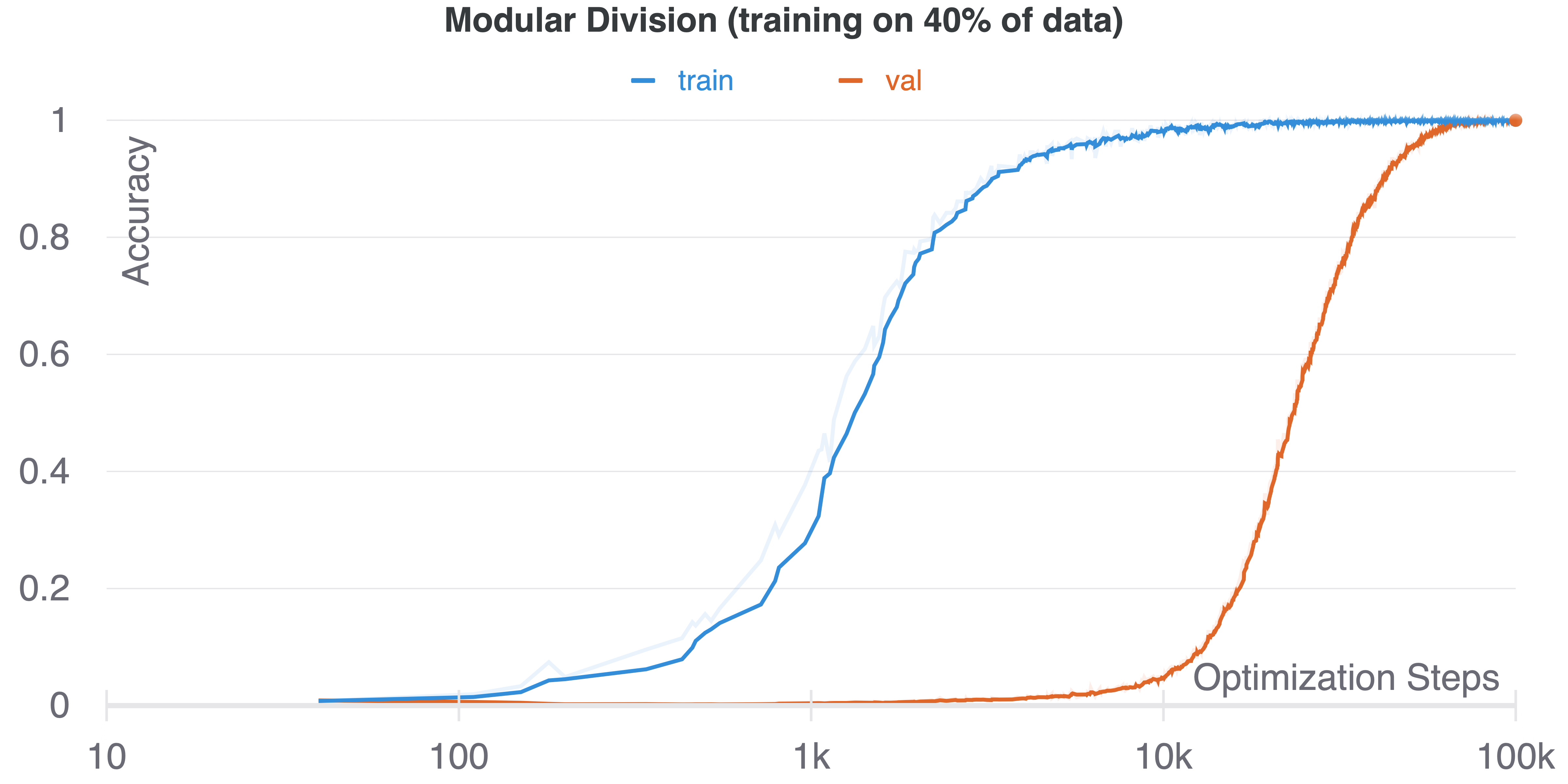
November 2021 [code] Re-create the dramatic train/test curves from the original paper; experiment with the grokking phenomenon yourself. |
|
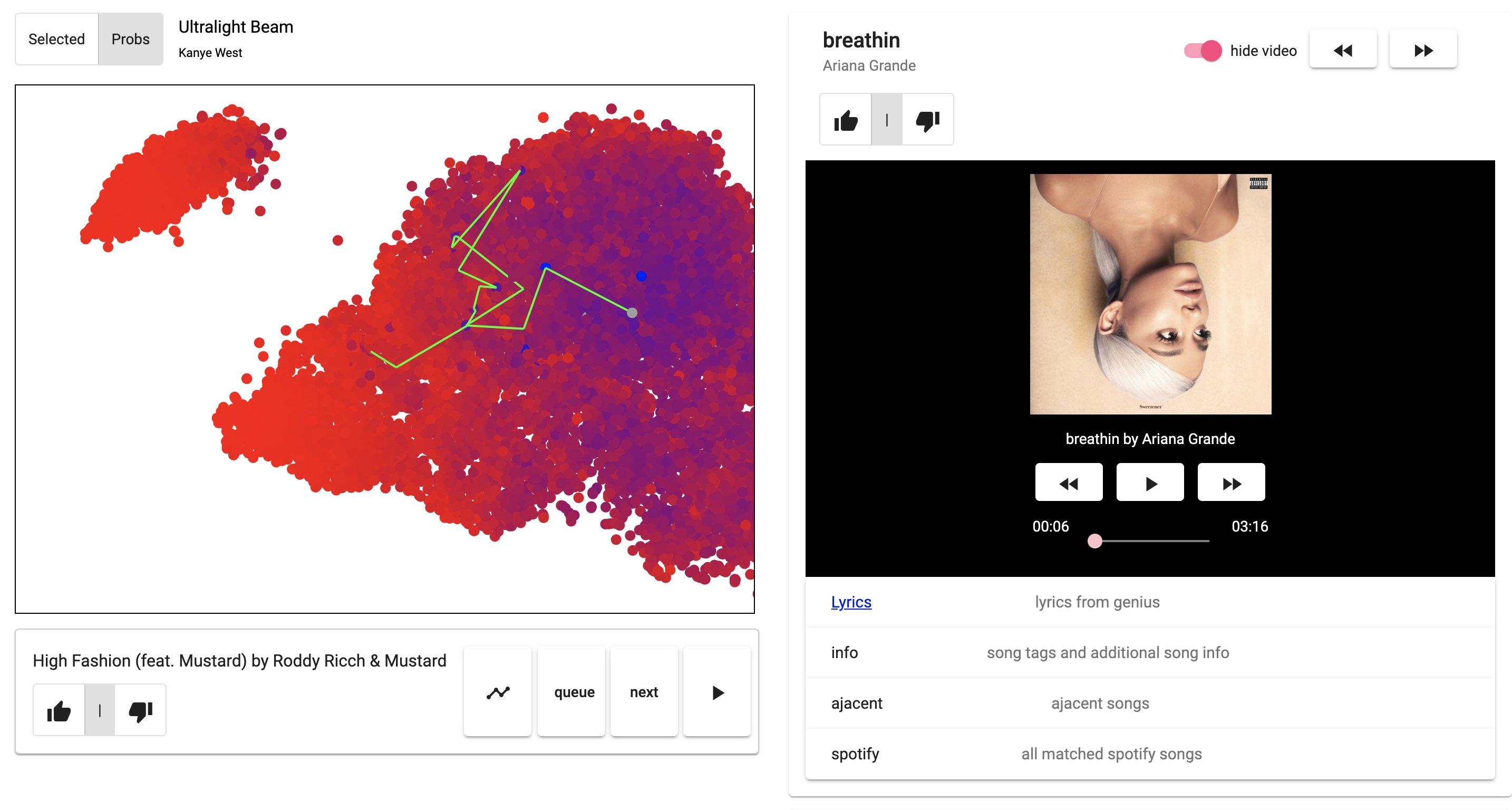
June-July 2020 [tweet] Harness the power of deep music representations to generate playlists and visualize your music preferences in an interactive web app. |
|
|
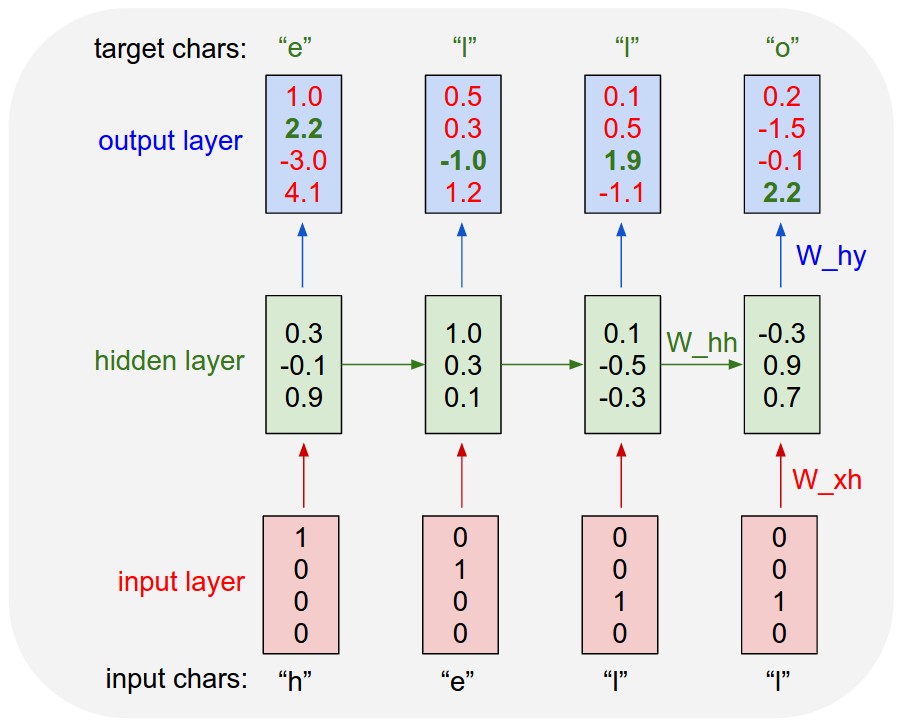
2017/2018 [code] A deep learning framework implemented from scratch in C++/OpenCL. Implements GPU kernels that can run on a 2013 Macbook Air GPU (and other Apple computers). Implements LSTM training/inference for music lyric generation. |
|
2017/2018 [app store] A humorous sound-box app. |

|
|
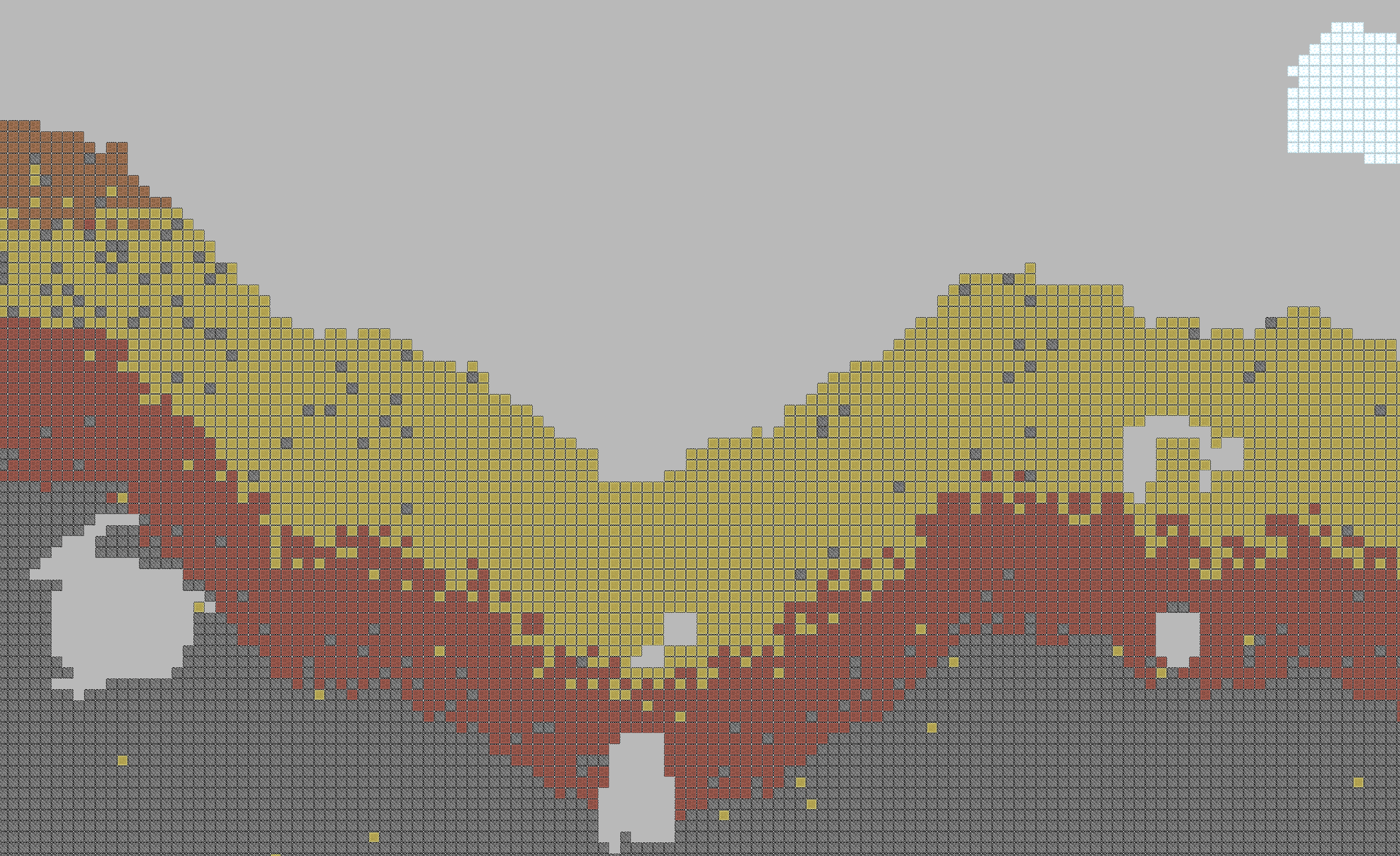
2015 [code] Scroll through an infinite 2D block-world consisting of rugged terrain, endless caves, fluffy clouds, and extreme biomes all synthesized by PRNGs and Perlin Noise. |
|
Website design from Jon Barron |